Prostate Cancer
Symptoms
Until a kidney stone moves into the ureter” the tube connecting the kidney and bladder” you may not know you have it. At that point, these signs and symptoms may occur:
Definition
Prostate cancer is cancer of the small walnut-shaped gland in males that produces seminal fluid, the fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men, affecting about one in six men in the United States. A diagnosis of prostate cancer can be scary not only because it can be life-threatening, but also because treatments can cause side effects such as bladder control problems and erectile dysfunction (impotence). But diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer have gotten much better in recent years.
Prostate cancer usually grows slowly and initially remains confined to the prostate gland, where it may not cause serious harm. While some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly. If prostate cancer is detected early” when it's still confined to the prostate gland” you have a better chance of successful treatment.
Symptoms
Prostate cancer usually doesn't produce any noticeable symptoms in its early stages, so many cases of prostate cancer aren't detected until the cancer has spread beyond the prostate. For most men, prostate cancer is first detected during a routine screening such as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test or a digital rectal exam (DRE).
When signs and symptoms do occur, they depend on how advanced the cancer is and how far the cancer has spread.
Early signs and symptoms of prostate cancer can include urinary problems, caused when the prostate tumor presses on the bladder or on the tube that carries urine from the bladder (urethra). However, urinary symptoms are much more commonly caused by benign prostate problems, such as an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or prostate infections. Less than 5 percent of cases of prostate cancer have urinary problems as the initial symptom. When urinary signs and symptoms do occur, they can include:
Trouble urinating
Starting and stopping while urinating
Decreased force in the stream of urine
Cancer in your prostate or the area around the prostate can cause:
Blood in your urine
Blood in your semen
Prostate cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes in your pelvis may cause:
Swelling in your legs
Discomfort in the pelvic area
Advanced prostate cancer that has spread to your bones can cause:
Bone pain that doesn't go away
Bone fractures
Compression of the spine
When to seek medical advice
If you have difficulties with urination, see your doctor. This condition doesn't always relate to prostate cancer, but it can be a sign of prostate-related problems.
Beginning at age 50, the American Cancer Society recommends having yearly screening tests for prostate cancer. If you're black or have a family history of the disease, you may want to begin at a younger age. Yearly screenings can help detect prostate cancer early, when it's easier to treat. They include:
PSA test. This blood test checks levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which can be a sign of prostate cancer. While this test can detect signs of cancer, elevated PSA levels are sometimes caused by conditions other than cancer, such as prostate enlargement, infection or inflammation.
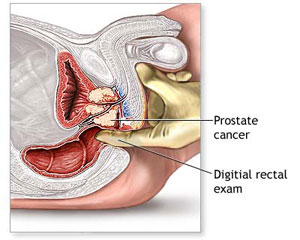
Digital rectal exam (DRE). This test involves insertion of a lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for bumps on the prostate. While it can be slightly uncomfortable, an annual DRE is a quick, simple exam that can be a lifesaver
Tests And Diagnosis
Prostate cancer may not cause any symptoms at first. The first indication of a problem may come during a routine screening test, such as:
Digital rectal exam (DRE). During a DRE, your doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum to examine your prostate, which is adjacent to the rectum. If your doctor finds any abnormalities in the texture, shape or size of your gland, you may need more tests.
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. A blood sample is drawn from a vein and analyzed for PSA, a substance that's naturally produced by your prostate gland to help liquefy semen. It's normal for a small amount of PSA to enter your bloodstream. However, if a higher than normal level is found, it may be an indication of prostate infection, inflammation, enlargement or cancer. Studies have not been able to show that routine screening decreases the chance that anyone will die of prostate cancer, but screening with PSA and DRE can help identify cancer at an earlier stage.
Trans rectal ultrasound. If other tests raise concerns, your doctor may use trans rectal ultrasound to further evaluate your prostate. A small probe, about the size and shape of a cigar, is inserted into your rectum. The probe uses sound waves to get a picture of your prostate gland.
Prostate biopsy. If initial test results suggest prostate cancer, your doctor may recommend biopsy. To do a prostate biopsy, your doctor inserts a small ultrasound probe into your rectum. Guided by images from the probe, your doctor uses a fine, spring-propelled needle to retrieve several very thin sections of tissue from your prostate gland. A pathologist who specializes in diagnosing cancer and other tissue abnormalities evaluates the samples. From those, the pathologist can tell if the tissue removed is cancerous and estimate how aggressive your cancer is.